IPPCAAS Systematically Summarizes the Latest Advances in RNA Modifications in Plant-Biotic Interactions
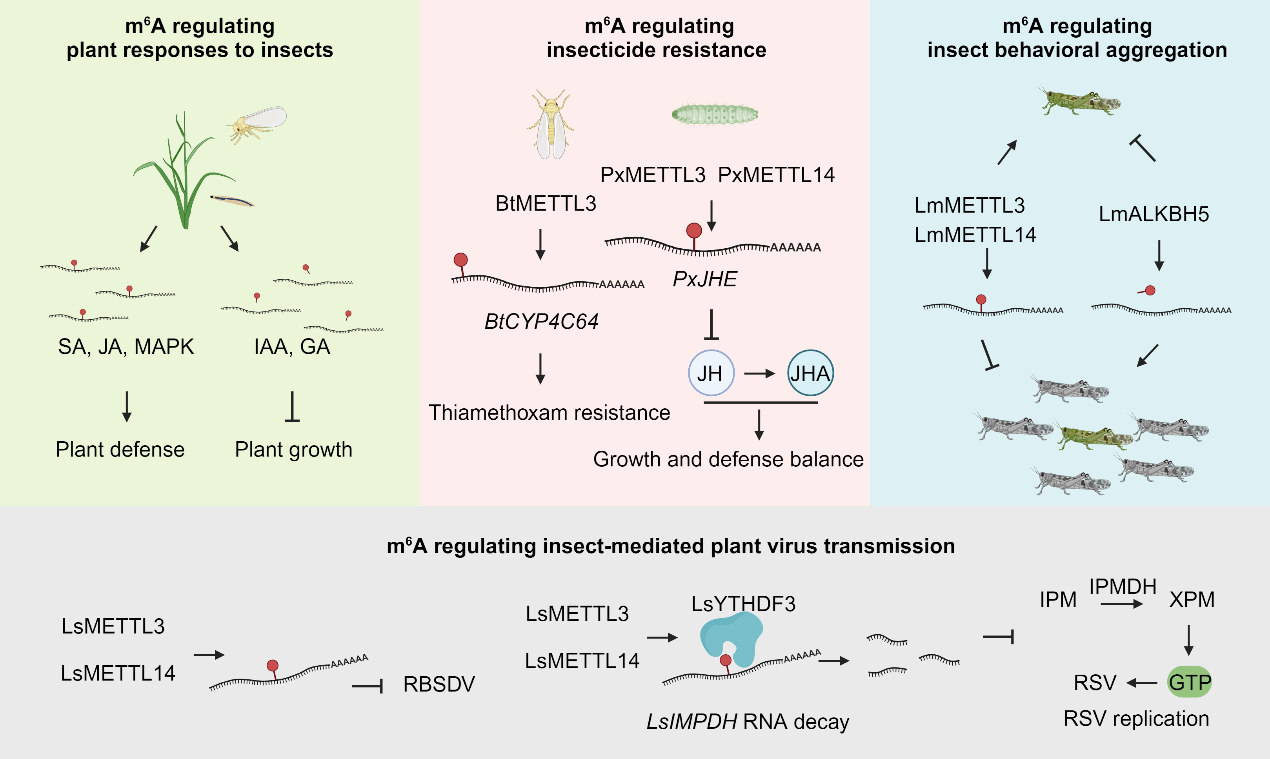
Recently, the Innovation Team for functional genomics of crop pathogens was invited to write a review article titled "RNA Modifications in Plant Biotic Interactions" for Plant Communications, a renowned journal under Cell. The paper summarizes the recent findings on the major RNA modifications identified in plants, with an emphasis on N6-methyladenosine (m6A), and discusses the functional significance of the effector components involved in m6A modification, and its diverse roles in plant biotic interactions, including plant-virus, plant-bacterium, plant-fungus, and plant-insect relationships. The article proposes constructing a high-precision RNA epitranscriptome map at single-base resolution and exploring plant pest and disease control using RNA editing technologies targeting RNA modifications. Furthermore, the article also highlights new technological developments that are driving research progress in this field and outlines new key challenges that remain to be addressed.
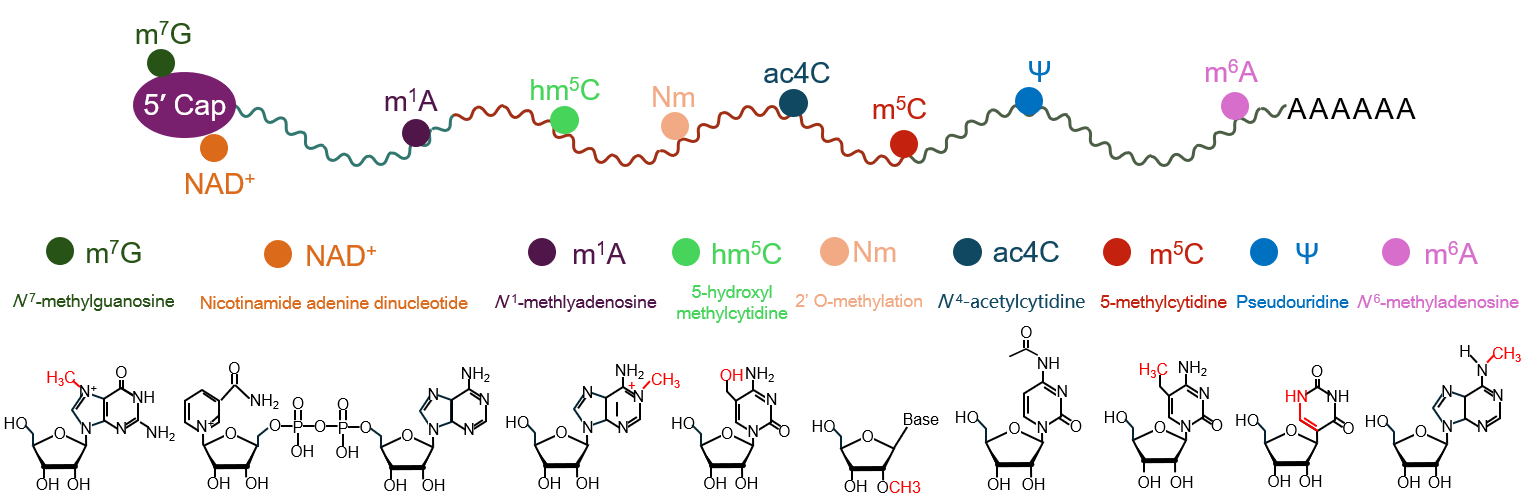
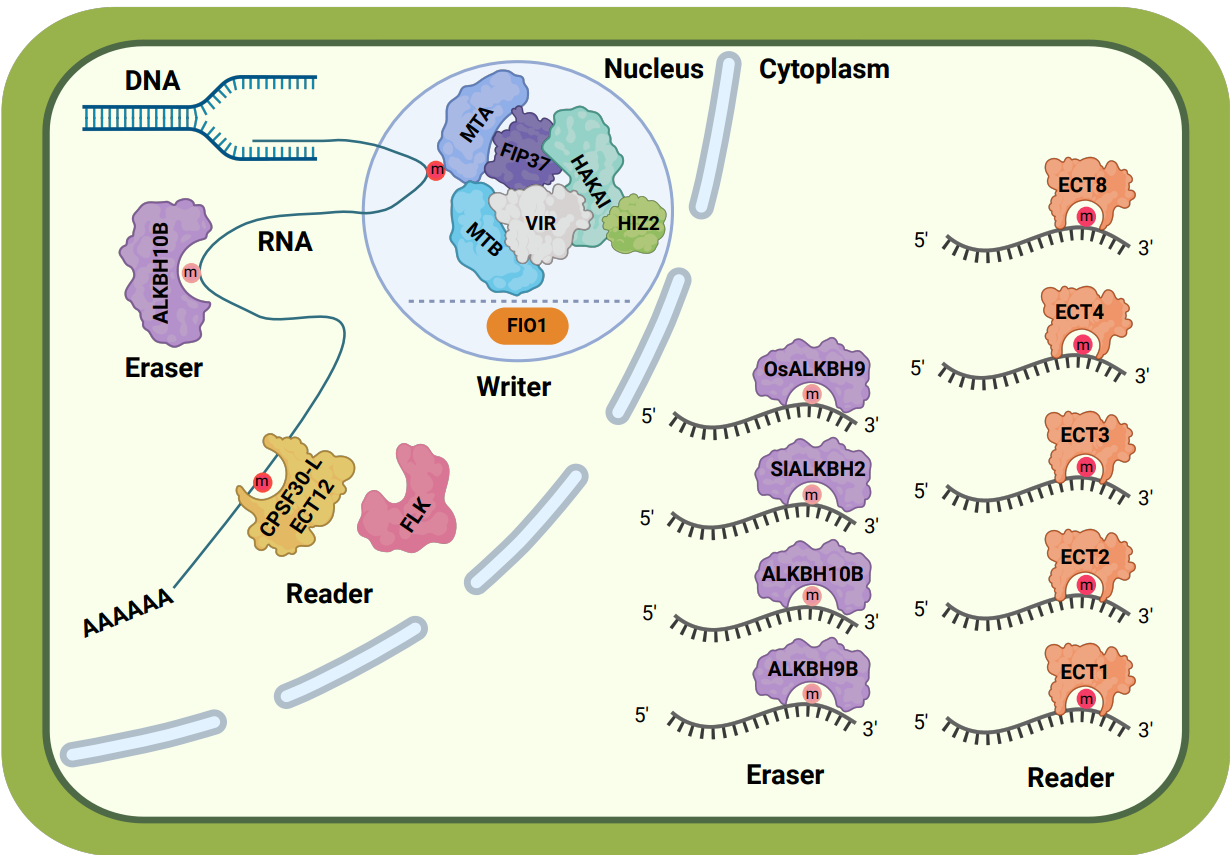
Chemical modifications on RNA molecules, collectively known as epitranscriptomic modifications, include N6-methyladenosine (m6A), a methylation modification at the nitrogen atom at the sixth position of adenosine. m6A modification is widely present in various RNA molecules such as rRNA, tRNA, and mRNA in eukaryotes and is the most abundant internal chemical modification in mRNA. It plays a crucial role in gene expression regulation.
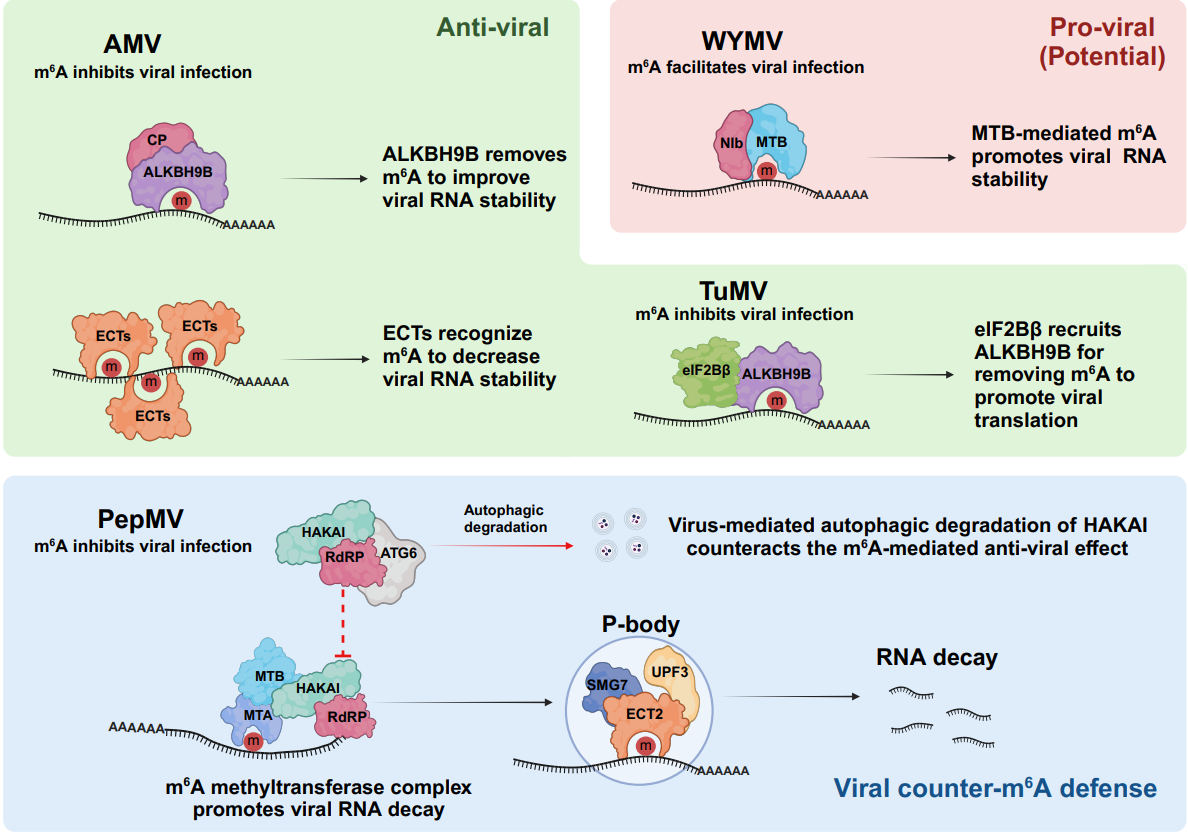
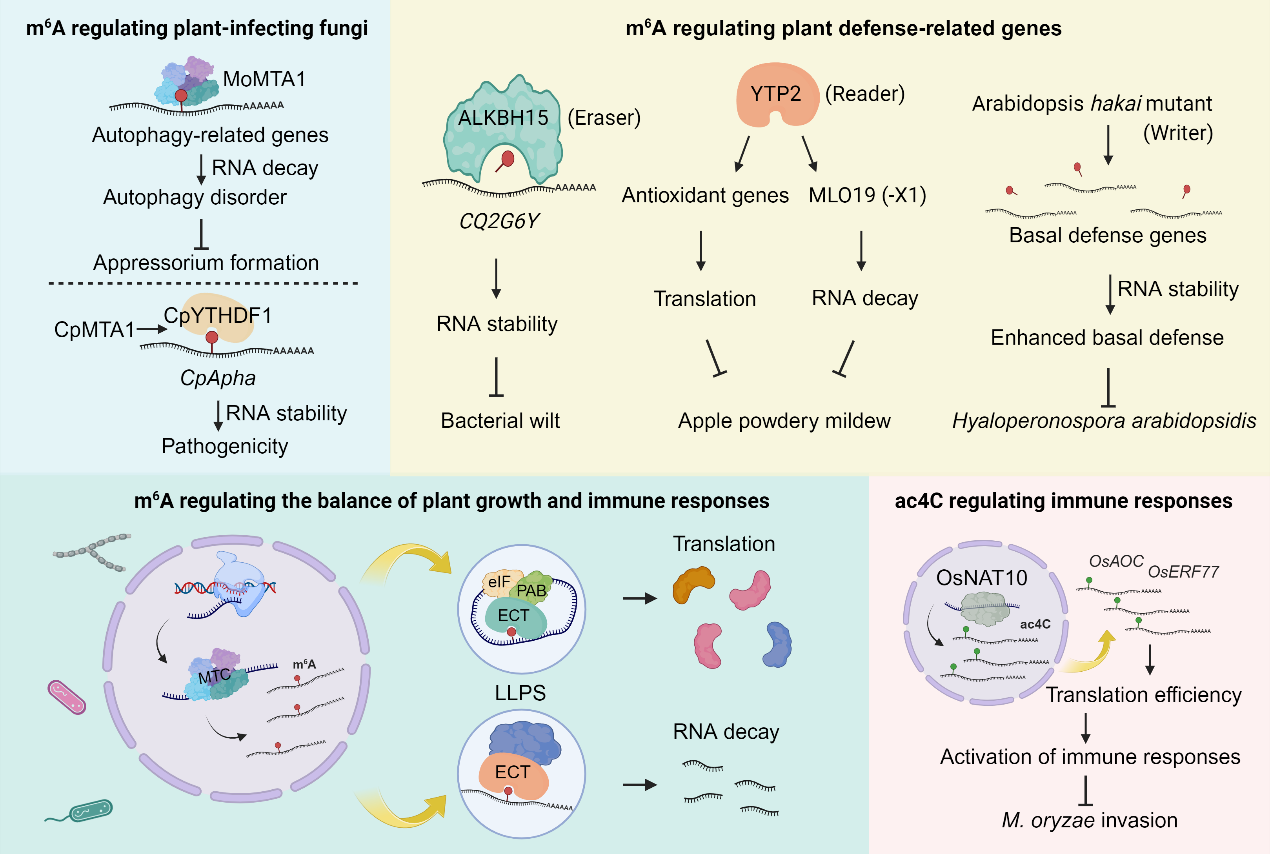
This review focuses on the effects of m6A and m5C modifications in plants, the associated effector proteins, and their functions. The important role of m6A modification in plant responses to biotic stresses is highlighted. For example, plant virus infections can induce dynamic changes in host endogenous m6A modifications, and the function of m6A varies in different plant viruses. Moreover, m6A modification can regulate the expression of plant defense-related genes, balancing plant growth and defense.
The paper was co-authored by Dr. Ge Linhao, a researcher at IPPCAAS, and Pan Fuan, a doctoral student at the College of Agriculture, Zhejiang University, as the joint first authors. Professor Zhou Xueping and Researcher Li Fangfang served as the corresponding authors. This research was supported by the National Key R&D Program and the National Natural Science Foundation.
Links: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39722456/
-
 China-CABI Project Development Workshop Held in Delémont, Switzerland
China-CABI Project Development Workshop Held in Delémont, Switzerland -
 The Lao PDR-China Joint Laboratory for Plant Protection holds technical seminar at IPPCAAS
The Lao PDR-China Joint Laboratory for Plant Protection holds technical seminar at IPPCAAS -
 IPPCAAS Successfully Organized the FAO-CAAS Technical Workshop on Sustainable Fall Armyworm Management for Africa in Guangdong
IPPCAAS Successfully Organized the FAO-CAAS Technical Workshop on Sustainable Fall Armyworm Management for Africa in Guangdong -
 IPPCAAS Hosts Symposium for CAAS-INARE International Joint Laboratory for Plant Protection to Congratulate Professor Emmanuelle Jacquin-Joly on Receiving the Chinese Government Friendship Award
IPPCAAS Hosts Symposium for CAAS-INARE International Joint Laboratory for Plant Protection to Congratulate Professor Emmanuelle Jacquin-Joly on Receiving the Chinese Government Friendship Award
