IPPCAAS Reveals a Molecular Mechanism for Rice Broad-Spectrum Disease Resistance Mediated by the Regulation of COP9 Signalosome Subunit Protein Homeostasis through Ubiquitination
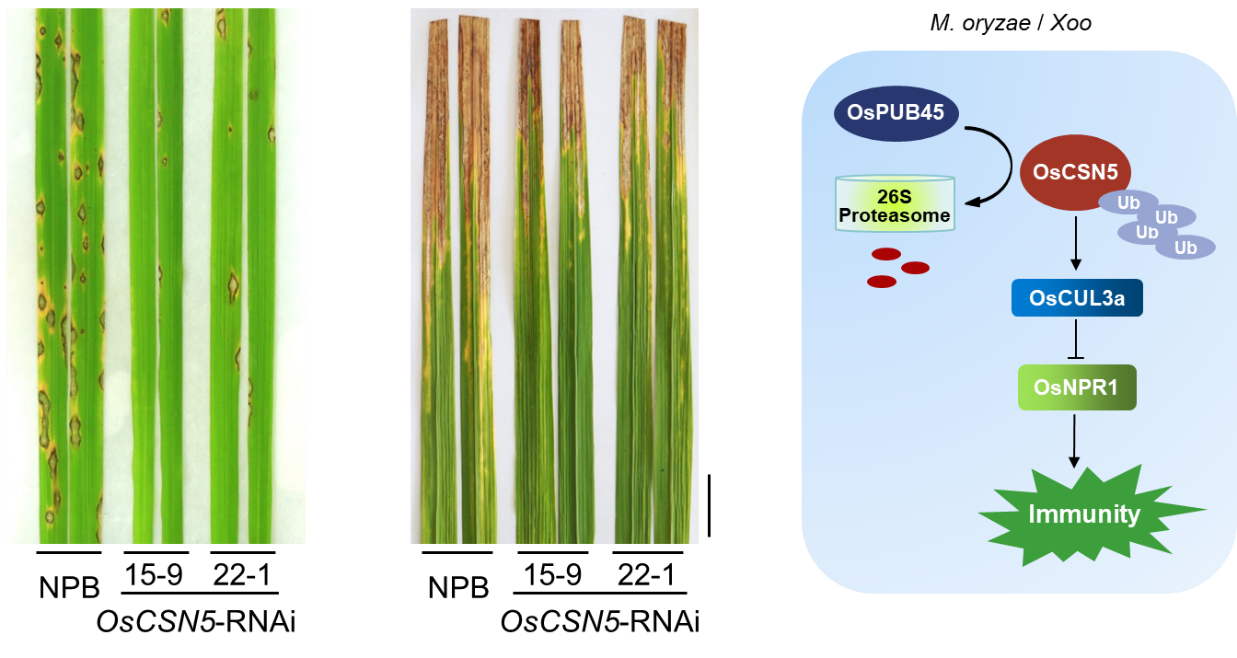
Recently, the Innovation Team for functional genomics of crop pathogens at the Institute of Plant Protection, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (IPPCAAS), published a research paper titled “Ubiquitination of OsCSN5 by OsPUB45 activates immunity by modulating the OsCUL3a-OsNPR1 module” in Science Advances. The study revealed a molecular mechanism by which the E3 ubiquitin ligase OsPUB45 regulates the OsCUL3a-OsNPR1 module through ubiquitination and degradation of OsCSN5, thereby modulating broad-spectrum disease resistance in rice.
The COP9 signalosome (CSN) is a highly conserved protein complex in eukaryotes, with CSN5 serving as its critical catalytic subunit. However, the role of CSN5 in plant immunity remain unclear. The study found that suppression of OsCSN5 in rice enhances resistance against the fungal pathogen Magnaporthe oryzea and the bacterial pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae Pv. oryzae without affecting growth. Using established rice E3 ubiquitin ligase library (UbE3), they found that an E3 ubiquitin ligase OsPUB45 interacts with OsCSN5, and ubiquitinates OsCSN5 for degradation via the 26S proteasome system. Further studies revealed that OsCSN5 stabilizes OsCUL3a, to promote the degradation of a positive regulator OsNPR1, negatively regulating resistance. Overexpression of OsPUB45 compromised accumulation of OsCUL3a, leading to stabilization of OsNPR1. Conversely, knockout of OsPUB45 destabilized OsNPR1.
The paper was co-authored by Dr. Zhang Chongyang, a postdoctoral researcher jointly trained by IPPCAAS and the Agricultural Genomics Institute at Shenzhen of CAAS (AGISCAAS), and Fang Liang, a doctoral student jointly trained by IPPCAAS and University of Liège, Belgium. Dr. Ning Yuese and Dr. Wang Ruyi from IPPCAAS served as the co-corresponding authors. Dr. Li Aihong and Dr. Xiao Ning from Jiangsu Lixiahe Agricultural Science Research Institute, Dr. Yang Jian from Ningbo University, and Dr. Ruan Jue from AGIS provide contributions. The study was supported by the National Key R&D Program, the National Natural Science Foundation, and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
Links: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adr2441
-
 China-CABI Project Development Workshop Held in Delémont, Switzerland
China-CABI Project Development Workshop Held in Delémont, Switzerland -
 The Lao PDR-China Joint Laboratory for Plant Protection holds technical seminar at IPPCAAS
The Lao PDR-China Joint Laboratory for Plant Protection holds technical seminar at IPPCAAS -
 IPPCAAS Successfully Organized the FAO-CAAS Technical Workshop on Sustainable Fall Armyworm Management for Africa in Guangdong
IPPCAAS Successfully Organized the FAO-CAAS Technical Workshop on Sustainable Fall Armyworm Management for Africa in Guangdong -
 IPPCAAS Hosts Symposium for CAAS-INARE International Joint Laboratory for Plant Protection to Congratulate Professor Emmanuelle Jacquin-Joly on Receiving the Chinese Government Friendship Award
IPPCAAS Hosts Symposium for CAAS-INARE International Joint Laboratory for Plant Protection to Congratulate Professor Emmanuelle Jacquin-Joly on Receiving the Chinese Government Friendship Award
