IPPCAAS Develops Solid Hydrogel Tablet to Reduce Drift Risk of Glyphosate Isopropylamine Salt
Recently, the Molecular Targets of Pesticides and Green Pesticide Innovation Team at the IPPCAAS has developed an alkyl-modified polyacrylic acid solid hydrogel tablet loaded with glyphosate isopropylamine salt, which can significantly reduce droplet drift risk during herbicide application. The findings were published in the Journal of Cleaner Production (Impact Factor 10.0) under the title "Alkyl-Modified Polyacrylic Acid Hydrogel Tablets for Targeted Retention and Reduced Droplets Drift of Glyphosate Isopropylamine Salt."
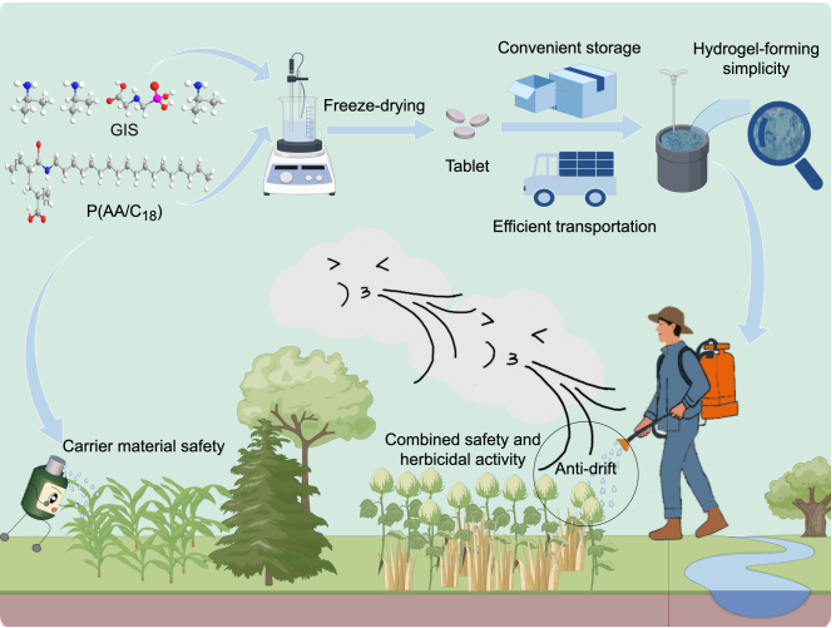
Hydrogels, with their unique three-dimensional network structure, show great potential in loading and controlled release of pesticide active ingredients and have become an important research direction in pesticide formulations. However, existing studies have mainly focused on their sustained and controlled-release properties, with limited systematic investigation into their role in regulating droplet drift behavior during application. Additionally, traditional fluid hydrogels face challenges in storage and transportation. Therefore, developing a solid hydrogel tablet that combines anti-drift performance with ease of application holds significant theoretical value and practical prospects for improving pesticide application efficiency and reducing environmental risks. It is expected to become an important technological pathway for promoting precise and safe pesticide use.
Glyphosate isopropylamine salt, as a broad-spectrum and low-cost herbicide, is widely used in global agricultural production. However, its application is constrained by non-target area contamination caused by droplet drift, which affects its environmental friendliness and application safety. To address this issue, this study successfully synthesized alkyl-modified polyacrylic acid through a simple amidation reaction between polyacrylic acid and octadecylamine. This material, when blended with glyphosate isopropylamine salt and processed via dilution and freeze-drying, formed a hydrogel tablet requiring no additional additives. The tablet offers multiple advantages, including ease of transportation, environmental friendliness, and low cost. The diluted hydrogel exhibited excellent rheological behavior, meeting the requirements for field spraying operations. Experimental results showed that the hydrogel effectively suppressed splashing and rebound of the solution on barnyardgrass leaves, enhanced adhesion on the leaf surface, and thereby increased the retention of active ingredients on the target. Wind tunnel tests further verified its anti-drift performance: at a distance of 4 meters from the nozzle, the droplet drift volume of the hydrogel system was reduced by 85.3% and 78.96% compared to the original aqueous solution and commercial aqueous formulation, respectively. Bioassay experiments demonstrated that the herbicide efficacy of the hydrogel tablet was comparable to that of commercial formulations, with no adverse effects on corn growth from the carrier material. Tests on glyphosate-resistant cotton further confirmed the good crop safety of this hydrogel-loaded system.
This study establishes a simple and efficient strategy for preparing herbicide-loaded hydrogel tablets, combining excellent anti-drift performance with convenient storage and transportation characteristics. It provides an innovative solution for achieving reduced pesticide use, enhanced efficacy, and precise delivery.
Ph.D. candidate Zhang Yingxi from the IPPCAAS is the first author of the paper, with Researcher Cao Lidong as the corresponding author. Researcher Huang Qiliang provided important guidance for the research. The work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China and the Agriculture Science and Technology Innovation Program..
-
 International Symposium on Plant Biosafety (ISPB 2025) Convenes in Guangzhou — Science-led plant health governance to secure food systems and advance the SDGs
International Symposium on Plant Biosafety (ISPB 2025) Convenes in Guangzhou — Science-led plant health governance to secure food systems and advance the SDGs -
 Three decades of China's membership of CABI celebrated at 2nd International Symposium on Plant Biosafety
Three decades of China's membership of CABI celebrated at 2nd International Symposium on Plant Biosafety -
 CABI receives recognition from FAO for its work to support sustainable plant production and protection
CABI receives recognition from FAO for its work to support sustainable plant production and protection -
 Second Round Notice | International Symposium on Plant Biosafety (ISPB 2025)
Second Round Notice | International Symposium on Plant Biosafety (ISPB 2025)
