IPPCAAS found Autophagy Core Proteins Regulate Rice Immunity via Autophagy-Independent Pathways
Recently, the Crop Pathogens Functional Genomics Research Innovation Team at the Institute of Plant Protection, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (IPPCAAS) published a paper in Molecular Plant entitled “OsATG1 and OsATG8 exhibit autophagy-independent functions to oppositely regulate ROP GTPase-mediated plant immunity in rice.”
The study demonstrated that two core autophagy proteins OsATG1 and OsATG8 in rice oppositely regulate the ROP GTPase-mediated immunity independent of the autophagy pathway. Specifically, OsATG1 phosphorylates the Rho GTPase-activating protein (RhoGAP) SPIN6, which enhances immune suppression by inactivating the ROP GTPase OsRac1 signaling. By contrast, OsATG8 competitively disrupts the OsATG1–SPIN6 complex, releasing SPIN6 inhibition and activating immunity; interestingly, the non-lipidated form of OsATG8 retained this competition ability and promotes rice immunity independent of autophagy. Further research revealed that rice immunity and the OsATG8 protein are induced under nutrient limitations, while SPIN6 is degraded. The OsATG1-mediated phosphorylation of SPIN6 blocks the nutrient limitation-induced immunity. This establishes a direct molecular link between nutritional status and immune activation, whereby the OsATG8–OsATG1–SPIN6 module responds dynamically to nutrient stress to fine-tune rice defense strategies.
This study uncovers the autophagy-independent functions of OsATG1 and OsATG8 in rice, demonstrating that they regulate a plant-specific ROP GTPase immune pathway in a opposite ways These findings expand the understanding of autophagy proteins and provide new genes and materials for improving crop disease resistance. Moreover, this discovery provides broader insights into the conserved immune homeostasis mechanisms across plants, animals, and humans.
Dr. Feng He, a joint postdoctoral fellow of IPPCAAS and the Agricultural Genomics Institute, is the first author of the paper. Prof. Yuese Ning (IPPCAAS) is the corresponding author. Prof. Yule Liu from Tsinghua University and other collaborators also contributed to this research. The project was supported by the Innovation Program of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation.
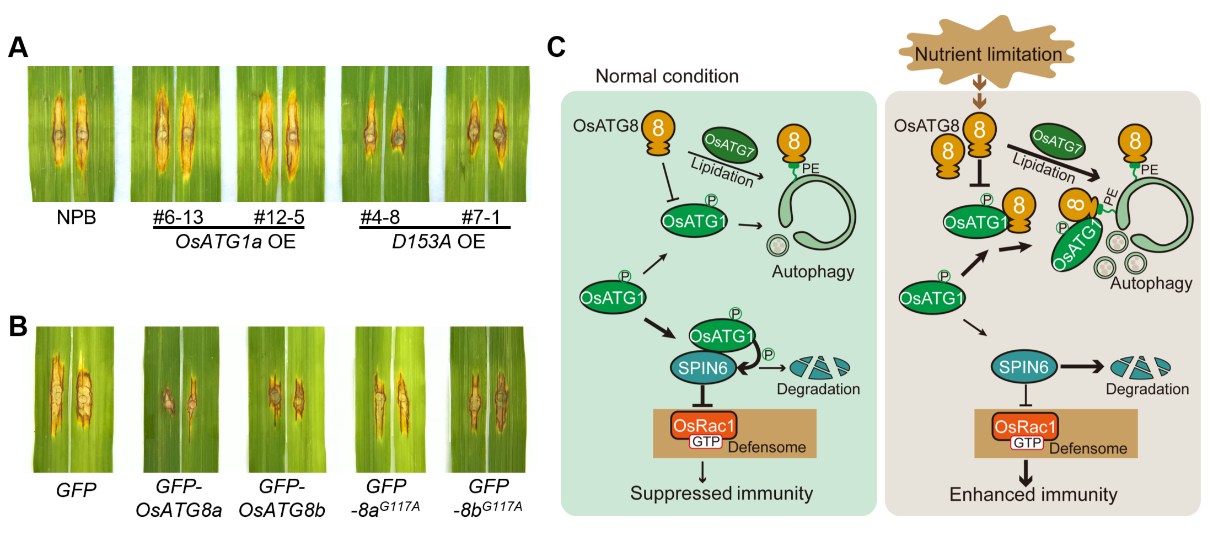
-
 IPPCAAS Expert Wins the Society for Invertebrate Pathology Early Career Award
IPPCAAS Expert Wins the Society for Invertebrate Pathology Early Career Award -
 Workshop on Green Control Technology for Corn Pests and Diseases in the Lancang-Mekong Region successfully held in Kunming
Workshop on Green Control Technology for Corn Pests and Diseases in the Lancang-Mekong Region successfully held in Kunming -
 IPPCAAS Experts Visit Australia to Promote In-Depth China–Australia Cooperation in Plant Biosafety
IPPCAAS Experts Visit Australia to Promote In-Depth China–Australia Cooperation in Plant Biosafety -
 China-France cooperation in plant protection was further strengthened
China-France cooperation in plant protection was further strengthened
