Scientists from IPPCAAS Reveal a Broad-spectrum Rice Blast Resistance Gene in Regulating Whole Growth Period
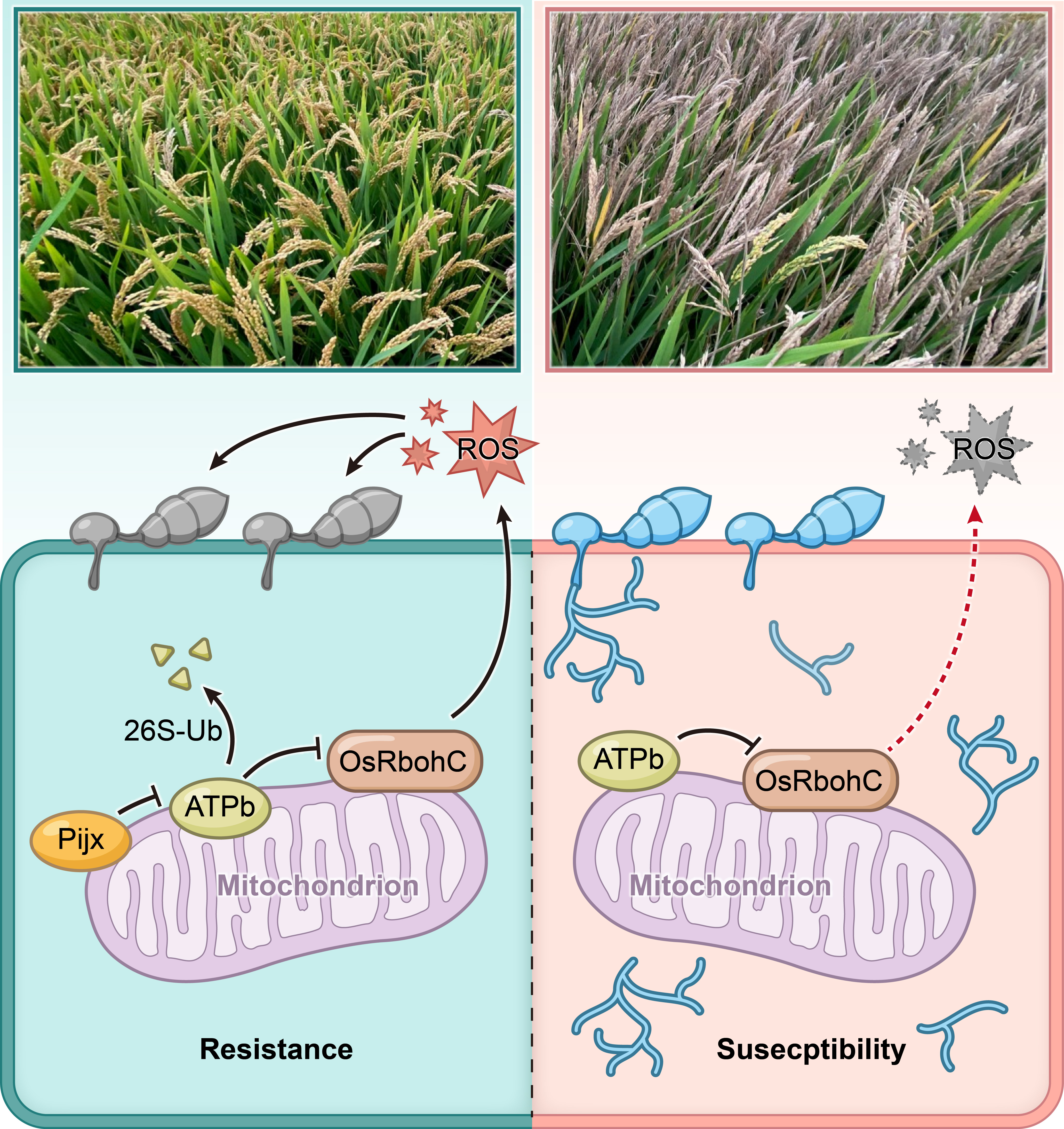
Recently, a paper entitled "Pijx confers broad-spectrum seedling and panicle blast resistance by promoting the degradation of ATP β subunit and OsRbohC-mediated ROS burst in rice" was published in the Molecular Plant Journal, by Prof. Ning Yuese’ research team at IPPCAAS, together with scientists from the Institute of Agricultural Sciences in Lixiahe Region, Jiangsu province. This study reported the rice blast resistance gene Pijx with broad-spectrum resistance (BSR) throughout the entire growth period of rice and investigated its molecular mechanism.
Rice blast, caused by the fungal pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae, is one of the most important diseases of rice. Utilization of blast-resistance genes is the most economical, effective, and environmentally friendly way to control the disease. However, genetic resources with BSR that is effective throughout the growth period of rice are rare.
In the study, using a genome-wide association study, the researchers cloned a new blast-resistance gene on chromosome 12, Pijx, which encodes a typical CC-NBS-LRR protein. Pijx is derived from wild rice species and confers BSR to M. oryzae at both seedling and panicle stages. Mechanistically, the LRR domain of Pijx interacts with and promotes the degradation of the ATP synthase β subunit (ATPb) via the 26S proteasome pathway. ATPb acts as a negative regulator of Pijx-mediated panicle blast resistance, and interacts with OsRbohC to promote its degradation. Interestingly, RNA-seq analysis showed that there are significant differences in Pijx and another resistance protein Piz-t mediated disease resistance pathways. The researchers subsequently generated PPLPijx Piz-t pyramided line carrying Pijx and Piz-t, which expands the resistance spectrum to panicle blast.
This research was supported by the grant of the International Cooperation and Exchange Program from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, etc.
Link to paper:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2023.10.001
-
 China-Laos Training Workshop on Integrated Management of Destructive Crop Pests and Diseases Successfully held in Laos
China-Laos Training Workshop on Integrated Management of Destructive Crop Pests and Diseases Successfully held in Laos -
 New Plant Protection: New challenge and new opportunity for plant protection
New Plant Protection: New challenge and new opportunity for plant protection -
 International and SELAMAT Conference on Pesticide Residue and Mycotoxin Contamination Held in Beijing
International and SELAMAT Conference on Pesticide Residue and Mycotoxin Contamination Held in Beijing -
 CAAS President Meets Chairman of ASEAN FAW Taskforce
CAAS President Meets Chairman of ASEAN FAW Taskforce
